Must-Know Terminal Commands for Mac Users
The mouse lets you click buttons and menus to perform tasks quickly and execute commands. Mac Terminal commands let you control your computer better. It allows users to type commands instead of clicking, which provides a faster way of doing tasks.
Learning the macOS command line lets you quickly check your system health, change directories, and manage apps, processes, and files. There are hundreds of Terminal commands available for users. Here is an important Mac Terminal commands cheat sheet that you should know.
Useful Terminal commands Mac for managing processes
Your Mac sometimes runs many background processes that might cause software freeze or sudden crash. Terminal commands help you list the background processes and terminate them. This avoids issues like the spinning ball and slowed computer. Follow this command prompt Mac.
Mac users should ensure they keep their computers running smoothly through proper maintenance. The advanced Terminal codes cannot run smoothly on a poorly maintained Mac. Enhanced maintenance requires Mac customization and organization. Manage startup processes and update software regularly. Clean the hardware to keep your Mac running as though it were new. CleanMyMac helps you remove unused apps and maintain the entire system. But, is CleanMyMac legit and secure for Mac computers? Yes, it is. This app is safe and legit ensuring your computer stays clean from all clutter.
Open the Mac Terminal in the Utilities app and type the command ps. This lists the active background processes. You may type ps aux for a detailed list.
Source: WikiHow
Name
ps — stdin stdout - file -- opt --help --version
Synopsis
ps [options]
The ps command displays information about your running processes, and optionally the processes of other users:
➜ ps
PID TTY TIME CMD
4706 ttys000 00:00:01 bash
15007 ttys000 00:00:00 emacs
16729 ttys000 00:00:00 ps
ps has at least 80 options; we’ll cover just a few useful combinations. To view your processes:
➜ ps -x
all of user smith’s processes:
➜ ps -u smith
all occurrences of a program:
➜ ps -axc | grep -w program_name
processes on terminal ttys000:
➜ ps -t s000
particular processes 1, 2, and 3505:
➜ ps -p 1,2,3505
and all processes and their threads:
➜ ps -axM
Next, type the command kill to close the processes. You can also terminate individual processes by name.
tim@Tims-MacBook-Pro ~ % ps -ax
PID TTY TIME CMD
1 ?? 3:09.69 /sbin/launchd
317 ?? 1:56.14 /usr/libexec/logd
318 ?? 0:00.05 /usr/libexec/smd
319 ?? 0:09.20 /usr/libexec/UserEventAgent (System)
321 ?? 0:01.36 /System/Library/PrivateFrameworks/Uninstall.framework/
322 ?? 1:43.46 /System/Library/Frameworks/CoreServices.framework/Vers
323 ?? 0:15.74 /System/Library/PrivateFrameworks/MediaRemote.framework
325 ?? 0:36.40 /usr/sbin/systemstats --daemon
327 ?? 0:41.96 /usr/libexec/configd
328 ?? 0:00.01 endpointsecurityd
329 ?? 1:30.92 /System/Library/CoreServices/powerd.bundle/powerd
330 ?? 0:01.98 /usr/libexec/IOMFB_bics_daemon
331 ?? 0:02.17 /System/Library/PrivateFrameworks/BiomeStreams.framewo
333 ?? 0:00.57 /usr/libexec/amfid
335 ?? 0:00.03 /usr/libexec/remoted
337 ?? 0:00.43 /usr/libexec/keybagd -t 15
338 ?? 0:00.34 /System/Library/PrivateFrameworks/MobileSoftwareUpdate
340 ?? 0:00.95 /usr/libexec/watchdogd
344 ?? 2:02.15 /System/Library/Frameworks/CoreServices.framework/Fram
345 ?? 0:00.08 /System/Library/CoreServices/iconservicesd
346 ?? 0:01.03 /usr/libexec/kerneleventagent
347 ?? 0:15.13 /usr/libexec/diskarbitrationd
Take note of the PID number next to the process you want to kill, then kill it by running the
kill PID
command. For example,
kill 3500
To kill a process immediately (also known as force quit) use
kill -9 3500
Navigate files with the macOS command line
Terminal codes let you list contents in a directory, print, or change it.
Type the cd command and folder name to open it quickly.
Example: Type cd Documents to open the Documents folder. To return to a previous folder, type cd …
Last login: Fri Jan 26 10:48:53 on ttys000
[connieyang@Yangs-Mac-mini ~ % cd ~/Documents
[connieyang@Yangs-Mac-mini Documents % ls
Archive-2023-19-01-19-08.zip
Archive-2023-58-03-58-34.zip
Documents 1
Screen Shot 2023-05-15 at 10.38.06 AM.png
Untitled.dmg
MagicMenu feedback.docx
Test
__________ 2
__________ 2.zip
[connieyang@Yangs-Mac-mini Documents % cd ..
[connieyang@Yangs-Mac-mini ~ % cd -
~/Documents
connieyang@Yangs-Mac-mini Documents %
Type ls, to display contents in a directory.
Use ls -a to view hidden folders.
Source: Catalin's Tech
Type pwd to view the exact directory.
pwd
Print Working Directory - the absolute pathname of the current folder (i.e. it tells you where you are).
Syntax pwd [-LP] Key -P The pathname printed contains no symbolic links -L The pathname printed can contain symbolic links.
Enabling the -o physical option for the set builtin command is equivalent to -P.
Use Mac Terminal commands cheat sheet to manage files
Mac Terminal codes for file management allow users to copy files, delete them, or move them quickly.
Type mv to move a file or remove it. Here is an example of a command prompt Mac to move or rename a file.
% mv ~/Downloads/MyFile.txt ~/Documents/Work/MyFile.txt You can also change the name of the file as it’s moved:% mv ~/Downloads/MyFile.txt ~/Documents/Work/NewFileName.txt
Use the command cp to copy files and paste them in another location. Type cp – file source – file destination. Type cp -r -source – destination to copy and paste an entire folder. For example, use this command to copy an Expenses folder to a Data folder on the Mac Terminal.
% cp -R ~/Documents/Expenses /Volumes/Data/Expenses
Type rm to delete a file or folder. The rm -r (folder) command deletes all folder content. The rm file.txt command deletes file.txt. Here is an example.
rm MyFile.rtf MyCV.rtf MyGreatAmericanNovel.rtfrm -i MyFile.rtf MyCV.rtf MyGreatAmericanNovel.rtf
Use the command prompt Mac to check system information
System information commands show important system data. It displays system health, macOS version, performance, and processes. Here are some important system information Terminal commands you should know.
- uname. Open Terminal in the Utilities app and type uname -a. This command displays the current macOS and kernel data. The command uname () displays your operating system. Here are other commands.
- top. To view system performance open Terminal and type the command top. This command displays the apps engaging the CPU or memory most. Pressing q quits the window.
- system_profiler. Displays hardware and software details
- df. Displays used and available disk space.
- vm_stat. displays RAM available space.
- char *sysname;
The name of the implementation of the operating system. - char *nodename;
The node name of this particular machine. The node name is set by the SYSNAME sysparm (specified at IPL), and usually differentiates machines running at a single location. - char *release;
The current release level of the implementation. - char *version;
The current version level of the release. - char *machine;
The name of the hardware type the system is running on.
Use Terminal codes to customize your Mac
Terminal commands allow you to change settings and personalize your computer. There are several ways to do this.
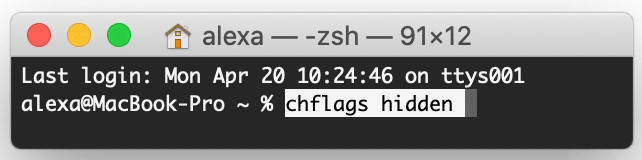
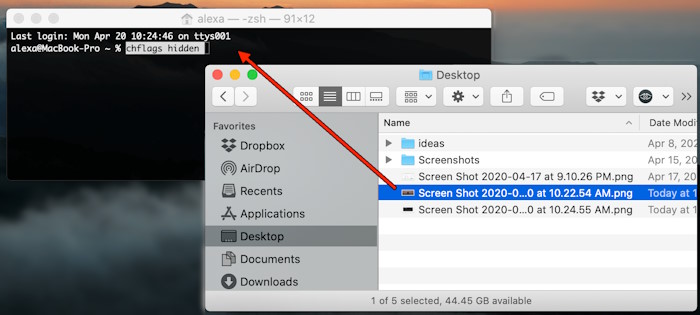
Type chflags hidden to hide files or keep folders hidden. To change macOS settings, type the command defaults write. Here is an example; the command “defaults write com.apple.finder appleshowallfiles TRUE” shows hidden files. Type chflags nonhidden (type file or folder name) to remove hidden settings. Hiding files enhances security and data privacy.
Open the Terminal app from Launchpad.
Type the following command and click Enter: chflags hidden
Then drag and drop the file you want to hide from Finder to Terminal, and click Enter.
Other important Terminal Commands
- chmod – example, chmod (permissions) (file) changes file permissions like sharing, read, and write.
- man lets you get help with using specific commands on Terminal. The information provides all the options for using the command.
- grep – example – grep (pattern) (file) displays the unique strings in a file.
- chown – example – chown (new_owner) (file) lets you change the owner’s name of a file.
- ping – example – ping (address) lets you text the strength of a specific network.
Conclusion
Terminal commands streamline your Mac workflow and enhance user experience. Learning them helps you manage files, and processes, and personalize the system. Start by learning the basics and progress to the advanced Terminal commands. Advanced functionalities let you optimize Mac performance and your productivity. Every command from killing processes to monitoring system health is important. It can transform your user experience, and cause a boost in work output.